Rootable의 개발일기
얕은 복제 vs 깊은 복제 본문
반응형
🔸 ArrayList 구현
package list.arrayList;
import interface_form.ListInterface;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayList<E> implements ListInterface<E>, Cloneable {
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //최소(기본) 용적 크기
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ARRAY = {}; //빈 배열
private int size; //요소 개수
Object[] array; //요소를 담을 배열
//생성자1 (초기 공간 할당x)
public ArrayList() {
this.array = EMPTY_ARRAY;
this.size = 0;
}
//생성자2 (초기 공간 할당o)
public ArrayList(int capacity) {
this.array = new Object[capacity];
this.size = 0;
}
private void resize() {
int array_capacity = array.length;
//if array's capacity is 0
if (Arrays.equals(array, EMPTY_ARRAY) {
array = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
return;
}
//용량 Fulled
if (size == array_capacity) {
int new_capacity = array_capacity * 2; //Doubling
//copy
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, new_capacity);
return;
}
//용적의 절반 미만으로 요소가 차지하고 있을 경우
if (size < (array_capacity / 2)) {
int new_capacity = array_capacity / 2;
//copy
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, Math.max(new_capacity, DEFAULT_CAPACITY));
return;
}
}
@Override
public boolean add(E value) {
addLast(value);
return true;
}
public void addLast(E value) {
//꽉차있는 상태라면 용적 재할당
if (size == array.length) {
resize();
}
array[size] = value; //마지막 위치에 요소 추가
size++;
}
@Override
public void add(int index, E value) {
//size보다 크면 빈 공간이 생김
if (index > size || index < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
if (index == size) { //마지막 위치에 삽입
addLast(value);
} else { //중간 삽입
if (size == array.length) { //Fulled
resize();
}
//index 기준 뒤에 있는 요소들 1칸씩 back
for (int i = size; i > index; i--) {
array[i] = array[i - 1];
}
array[index] = value; //index 위치에 요소 삽입
size++;
}
}
public void addFirst(E value) {
add(0, value);
}
@SuppressWranings("unchecked")
@Override
public E remove(int index) {
if (index >= size || index < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
E elem = (E) array[index];
array[index] = null; //삭제
//빈 공간 메꾸기
for (int i = index; i < size - 1; i++) {
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = null;
}
size--;
resize();
return elem;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object value) {
int index = indexOf(value);
if (index == -1) {
return false;
}
remove(index);
return true;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public E get(int index) {
if (index >= size || index < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return (E) array[index];
}
@Override
public void set(int index, E value) {
if (index >= size || index < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else {
//해당 위치의 요소를 교체
array[index] = value;
}
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object value) {
return indexOf(value) > -1;
}
//front -> back 탐색
@Override
public int indexOf(Object value) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i].equals(value)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//back -> front 탐색
public int lastIndexOf(Object value) {
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (array[i].equals(value)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public void claer() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = null;
}
size = 0;
resize();
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//새로운 객체 생성
ArrayList<?> cloneList = (ArrayList<?>)super.clone();
//새로운 객체의 배열도 생성해주어야 함 (객체는 얕은 복사가 되기 때문)
cloneList.array = new Object[size];
//배열의 값을 복사(Deep cloning)
System.arraycopy(array, 0, cloneList.array, 0, size);
return cloneList;
}
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(array, size);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size) {
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(array, size, a.getClass());
}
System.arraycopy(array, 0, a, 0, size);
return a;
}
}
✅ 테스트
package list.arrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayListApplication {
ArrayList<Integer> original = new ArrayList<>();
original.add(10);
ArrayList<Integer> copy = original;
ArrayList<Integer> clone = (ArrayList<Integer>) original.clone();
copy.add(20);
clone.add(30);
System.out.println("original list");
for (int i = 0; i < original.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("index " + i + " data = " + original.get(i));
}
System.out.println("\ncopy list");
for (int i = 0; i < original.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("index " + i + " data = " + copy.get(i));
}
System.out.println("\nclone list");
for (int i = 0; i < original.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("index " + i + " data = " + clone.get(i));
}
System.out.println("\noriginal list reference : " + original);
System.out.println("copy list reference : " + copy);
System.out.println("clone list reference : " + clone);
ArrayList<String> bucket = new ArrayList<>();
bucket.add("apple");
bucket.add("banana");
bucket.add("orange");
bucket.add(1, "strawberry");
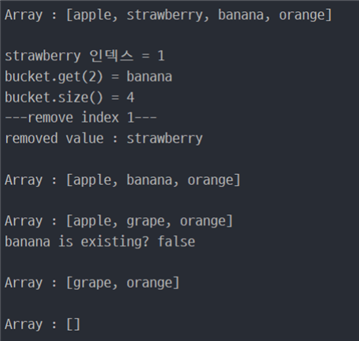
System.out.println("\nArray : " + Arrays.toString(bucket.toArray()));
System.out.println("\nstrawberry 인덱스 = " + bucket.indexOf("strawberry"));
System.out.println("bucket.get(2) = " + bucket.get(2));
System.out.println("bucket.size() = " + bucket.size());
System.out.println("---remove index 1---");
System.out.println("removed value : " + bucket.remove(1));
System.out.println("\nArray : " + Arrays.toString(bucket.toArray()));
bucket.set(1, "grape");
System.out.println("\nArray : " + Arrays.toString(bucket.toArray()));
System.out.println("banana is existing? " + bucket.contains("banana"));
bucket.remove("apple");
System.out.println("\nArray : " + Arrays.toString(bucket.toArray()));
bucket.clear();
System.out.println("\nArray : " + Arrays.toString(bucket.toArray()));
}

clone 메서드는 Object 클래스에서 객체의 클로닝을 위해 제공하는 메서드다.
원래 clone 메서드는 원본의 실제 값이 아닌 주소 값만 복사하여 동일 객체를 가리키는 Shallow cloning(얕은 복제)로 동작한다. 하지만 위 코드에서는 new를 통해 새로운 주소의 객체를 생성했으므로, original 객체에 영향을 주지 않았다.
🗨 얕은 복제(Shallow cloning) vs 깊은 복제(Deep cloning)
얕은 복제는 객체의 주소 값만을 복사하고, 깊은 복제는 원본 객체의 실제 상태 값만을 복사한다.
따라서, 원본과 영향을 주고받는 얕은 복제와 달리 깊은 복제는 원본과 다른 주소를 가진 객체를 생성하게 된다.
References:
https://st-lab.tistory.com/146
자바 [JAVA] - List Interface (리스트 인터페이스)
자료구조 관련 목록 링크 펼치기 더보기 0. 자바 컬렉션 프레임워크 (Java Collections Framework) 1. 리스트 인터페이스 (List Interface) - [현재 페이지] 2. 어레이리스트 (ArrayList) 3. 단일 연결리스트 (Singly Li
st-lab.tistory.com
반응형
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LIFO 구조와 ArrayDeque (0) | 2024.05.11 |
|---|---|
| Queue (0) | 2024.05.10 |
| List (0) | 2024.05.08 |
| Java Collection Framework (0) | 2024.05.08 |
| 직렬화와 역직렬화 (0) | 2024.05.03 |




