알고리즘
버블 정렬(Bubble Sort)
dev-rootable
2023. 10. 26. 11:47
반응형
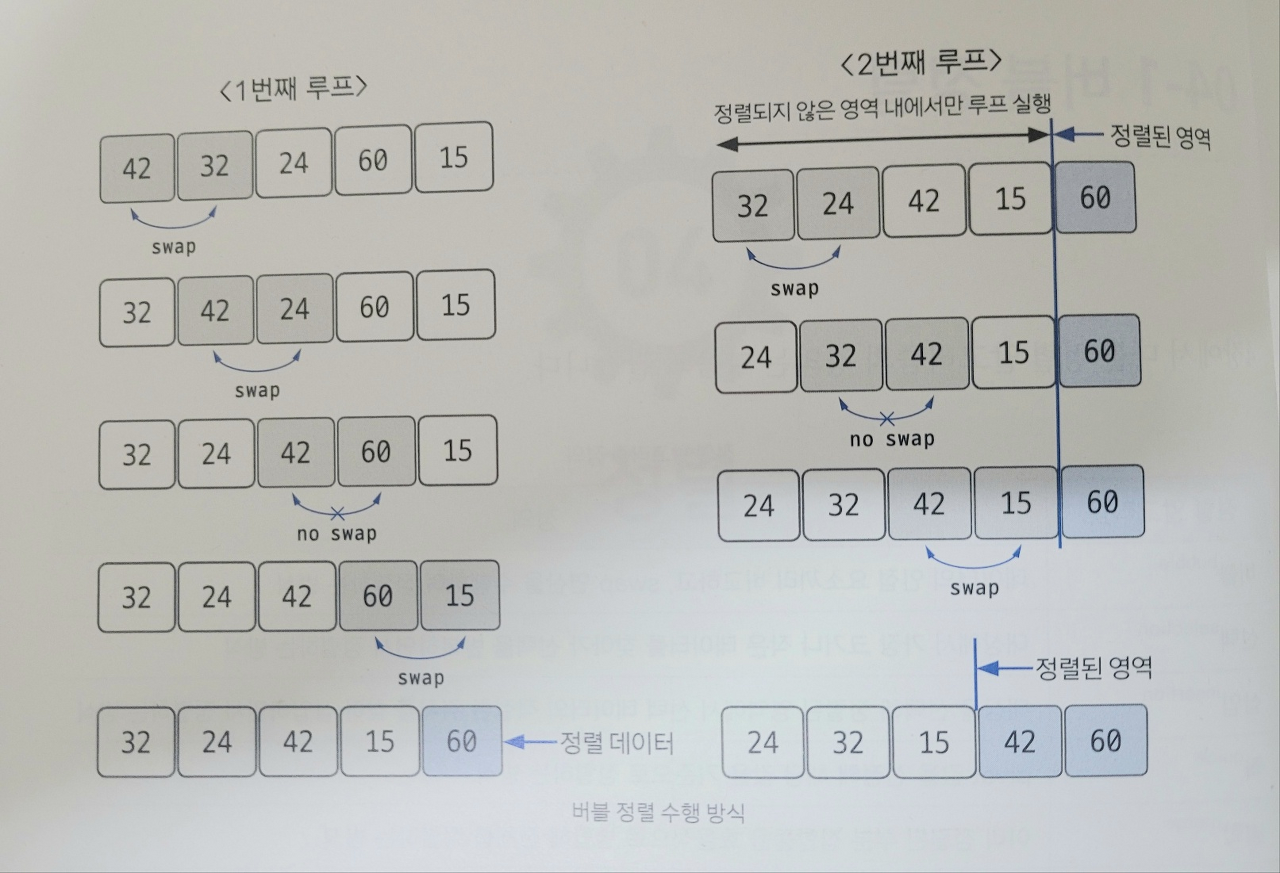
데이터의 인접 요소끼리 비교하고, swap 연산을 수행하며 정렬하는 방식
시간 복잡도: O(N^2)
📌 정렬 과정
- 비교 연산이 필요한 루프 범위를 설정
- 인접한 데이터 값을 비교
- swap 조건에 부합하면 swap 연산
- 루프 범위가 끝날 때마다 2~3 반복
- 정렬 영역을 설정한다. 다음 루프를 실행할 때는 이 영역을 제외
- 비교 대상이 없을 때까지 1~5 반복
만약 특정한 루프의 전체 영역에서 swap이 한 번도 발생하지 않았다면 그 영역 뒤에 있는 데이터가 모두 정렬됐다는 뜻이므로 프로세스를 종료해도 됨
📌 알고리즘
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int N = readInt();
int[] A = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) A[i] = readInt();
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
int swapCnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N - 1 - i; j++) {
if (A[j] > A[j + 1]) {
swapCnt++;
int tmp = A[j];
A[j] = A[j + 1];
A[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
if (swapCnt == 0) break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
bw.write(A[i] + "");
bw.newLine();
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
static int readInt() throws IOException {
int n = 0;
boolean isNegative = false;
while (true) {
int input = System.in.read();
if (input <= 32) {
return isNegative ? n * -1 : n;
} else if (input == '-')
isNegative = true;
else
n = (n << 3) + (n << 1) + (input & 15);
}
}
}
Reference:

반응형